Measurements and data acquisition in rain overflow basins
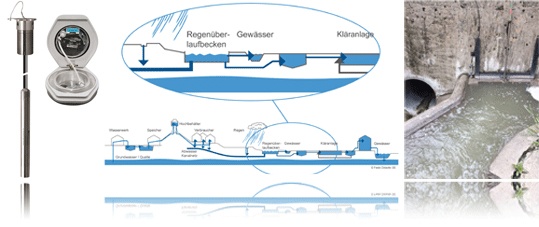
The European Water Framework Directive of 2000 resulted in various measures to improve the ecological and chemical conditions of surface waters. Quite a few measures are aimed directly at the ecologically sensitive nodes of the sewer network and sewage treatment plants to open water systems. This applies in particular to stormwater overflow basins and catch basins. Continuous basins keep the precipitation in the basin during heavy rain events, since the clarification basins can only hold a certain amount of wastewater. If the volume in the flow basin is full, a partial amount may be returned to the water, i.e. the basin is relieved. Solids / sludge etc. must be deposited beforehand. The sedimentation effect is absent in catch basins, since here only a drain into the watercourse is provided when the basin is fully filled without inlet to sewage treatment plants.
In the German Water Management Act, a reduction in the pollutant load according to the state of the art is required for wastewater discharges and the requirements are shown in the Wastewater Ordinance on a nationwide basis. For the treatment and discharge of rainwater, the requirements are regulated at the state level.
According to the Self-Monitoring Ordinance (EÜV 1995), measured values in Bavaria must be regularly evaluated by the operator and submitted to the responsible water authority.
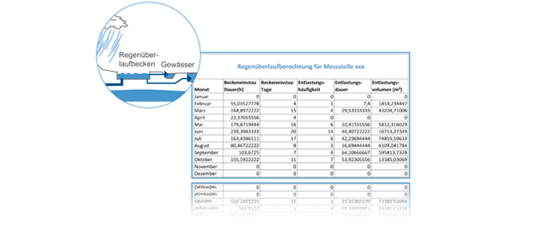
Essentially, the following data is compiled in an annual report: frequency of overflow events, duration of overflow events and volume of the discharged mixed water. Monitoring devices log the frequency and duration of impoundment and overflow events. If a rain overflow basin shows excessive relief activity, rapid action may be required due to the threat of water pollution from material or hydraulic overload.
Systems of measuring devices
According to the Self-Monitoring Ordinance (EÜV 1995), measured values in Bavaria must be regularly evaluated by the operator and submitted to the responsible water authority.
Essentially, it is the compilation of the following data in an annual report: frequency of overflow events, duration of overflow events and volume of the discharged mixed water. Monitoring devices log the frequency and duration of impoundment and overflow events. If a rain overflow basin shows excessive relief activity, rapid action may be required due to the threat of water pollution from material or hydraulic overload.
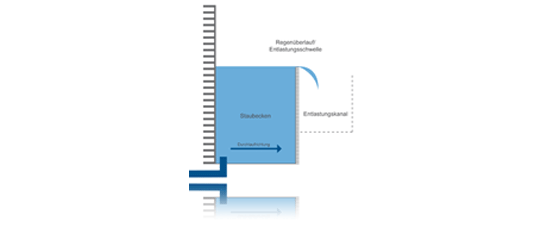
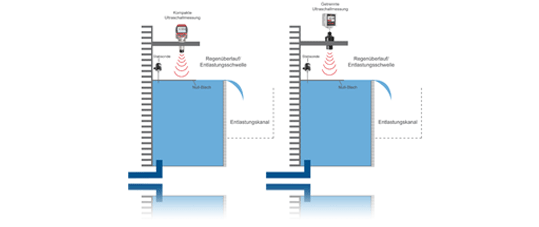
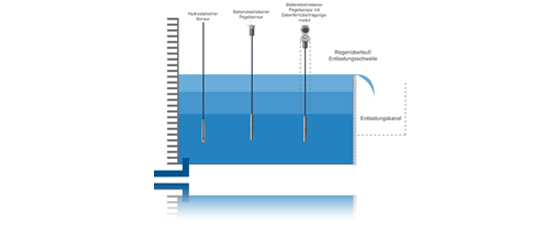
Contactless ultrasonic sensors are attached at a suitable distance above the relief threshold and the transit time of the ultrasonic signals and thus the pool level is measured. The ultrasonic signals rejected by the sensor are thrown back by the medium and recorded again by the sensor. The path is calculated based on the running time, the installation height is deducted and the level of the pool is obtained.
In the case of battery-operated measuring points, measurements are usually carried out in a longer measuring interval, e.g. 15 minutes, due to the power consumption. However, in order to be able to carry out a more precise measurement data collection in the event of a build-up or relief, the recording density is switched over in part via alarm thresholds or external transmitters such as float switches.
An additional method to measure the relief behavior or the relief duration is the combination of an ultrasonic sensor with zero plate and a rod probe. With this measurement, the head of the runoff at the relief threshold is recorded. And thus the runoff into water is determined. So that only levels above the relief threshold are measured, the threshold is marked with a zero plate. A rod probe can also be used to improve the measurement times. In its function as a conductive limit switch, the ultrasonic measurement is permitted shortly before the zero sheet.
This procedure makes sense above all if a quantity balance of the relieved mixed water is to be carried out. In some cases, however, the authorities in Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg in particular are pursuing a different objective. Here, particular attention is paid to the frequency and duration of the relief. According to the applicable leaflets, the relief point is then assigned a hysteresis of 3 to 5 cm in order to mask out wave movements in the pelvis. Although this can make sense for the duration and frequency, it makes a quantity measurement impossible. The manufacturers of the measuring devices and evaluation software solutions are therefore required to work with both calculations in the background. This means that you can work with hysteresis for the discharge duration and frequency and without hysteresis for calculating the amount.
The advantage of ultrasonic measurement lies in the simple installation and commissioning. Thanks to the non-contact measurement, ultrasonic sensors are long-term stable and easy to maintain.
However, constant, smooth media surfaces are required for the measurement. Foam and crackling rain can lead to measurement inaccuracies. Strong winds can also influence the direction of the ultrasonic signals. Therefore, the use of ultrasonic measurements in rain overflow basins should be checked carefully and the installation situation should be adapted accordingly.
Contactless radar measurements work with radar signals that are emitted by the sensor and reflected by the medium. The running time gives the distance covered and the filling level can be calculated by the radar software while masking out interfering signals. Compared to the ultrasonic system, foam formation has a little less influence on the measurement accuracy, but can still lead to measurement errors.
The tank fill level is determined with hydrostatic sensors. The hydrostatic pressure of the liquid column causes the measuring membrane to deflect. This is measured and converted into an electrical signal.
Due to the age-related, so-called zero point drift, hydrostatic sensors can deviate from the zero value at normal air pressure. Because of this, recalibrations are necessary to ensure reliable measurement results. Compared to non-contact measuring systems, measurement inaccuracies can occur if contaminants adhere to the sensor after contact with silted or dirty water and dry out or there is calcification. However, since these are rain overflow basins with rainwater and these are dry for most of the year, the probability of this is very low. Visual and functional checks are necessary for both measuring systems at appropriate intervals.
Hydrostatic sensors are widely used. Many providers specialize in this and offer robust, long-term stable sensors with different accuracy classes.
A special variant are battery-operated hydrostatic sensors with remote data transmission modules, because thanks to the latest technology, they offer long running times without maintenance and there are no investment costs for electricity and telephone connections.
Data can be transmitted by manual data collection using a laptop, handheld PC, USB stick, Bluetooth® device or the like. Another option is remote data transmission via the cellular network, e.g. directly to an internet platform if the sensor is connected to a remote data transmission module. The measuring points do not need to be visited personally. The data is forwarded by remote transmission. Remote data transmission modules are also capable of remote alarming via SMS or email.
Measurement data acquisition
In principle, measurement data should be logged regularly, at least once a month, and checked for plausibility.
Only by looking at the recorded data on a monthly basis can it be prevented that, for example, due to the failure of the water level measurement or due to measurement errors, no or no useful measurement data is available for a longer period of time. A simple plausibility check shows: if it has not rained at all in a month, no relief events may occur. On the other hand, if it has rained a lot, the overflow activity should be increased. Exceptional cases should be understandable.
Implausible data allow conclusions to be drawn about the functionality of the devices and therefore a regular check of the data should be carried out, since under certain circumstances a whole year of measured values for the data evaluation can be lost if a readout takes place only once a year.
The preparation for the annual report to the responsible water authority is facilitated by special software that carries out the rain overflow calculation and logging according to §5 of the Self-Monitoring Ordinance (EüV). The values for pool retention, pool relief and sliding min-max values are specified or calculated. Many calculation formulas are already stored in the software or can be adapted to the circumstances via user linearization.